Hair transplantation surgery removes baldness in certain areas but does not prevent further hair loss in non-transplanted areas. If the person experiences progressive hair loss in untreated areas, this can create an imbalance and make the overall result less satisfactory after two years.
Although hair transplantation is generally considered permanent, some people may experience hair loss even after the procedure.

Causes of hair transplant failure after 2 years
Common causes of hair loss within 2 years after hair transplantation are the following:
- Various diseases, including autoimmune disorders and hormone abnormalities, can jeopardise the outcome of a hair transplant. These diseases can prevent the survival and growth of hair follicles, resulting in poor hair growth or failure of the transplantation.
- Inadequate harvesting or transplantation methods can cause long-term hair loss. If the hair transplantation operation is performed by an inexperienced or unqualified surgeon, the grafts may not be placed correctly or may not survive the transplantation. As a result, the transplanted hair may grow poorly or not grow at all.
- Failure to follow the surgeon's instructions after hair transplantation, such as avoiding strenuous exercise, excessive sun exposure, or not taking prescribed medications correctly, may cause the transplant to fail.
- Hormonal fluctuations associated with ageing or underlying medical conditions can affect hair health.
- Genetic predisposition to baldness can affect both transplanted and non-transplanted hair.
- The effectiveness of a hair transplantation depends on the transplanted hair follicles receiving sufficient blood supply. Compromised blood supply to the grafts during or after treatment can lead to poor hair growth or loss of transplanted hair.
- Failure to maintain good hygiene and sterile conditions during the procedure may cause infections and damage the transplanted hair follicles.
- An insufficient amount of healthy hair follicles in the donor area may cause limited or thinning hair growth after two years.
Post-operative care
Things to be considered after hair transplant are as follows:
- Sleep in a semi-sitting position with your head over your heart for the first three nights.
- Use sterile medical water for the first 5 days and then mineral water10.
- Do not consume alcohol for the first 3 days.
- Do not pour tap water on the procedure site for the first 3 days.
- Do not do heavy exercise, gym, aerobics, heavy weight lifting or yoga for one week.
- Do not bend down to tie shoes or pick something up from the floor for the first 3 days.
- Do not use a hair dryer.
- Do not scratch the treated area with your fingernails.
- Do not allow the comb teeth to touch the treatment area when combing.
- Do not apply ice or cold packs to the treated area, forehead, or any part of the face.
Medication
Pain medication is given after surgery, but often only for a day or two. Medications can be given to prevent swelling, and keeping the head elevated also helps prevent swelling.
Washing
It is important to wash the hair regularly after surgery. If washing is done as recommended, the grafts are unlikely to dislodge. Washing helps to remove dirt, blood, and oil and gently removes any crusts or scales that form on the recipient areas.
Proper hygiene also helps prevent infection. The hair is wetted with a sterile solution, and shampoo is applied to the transplanted area with a piece of sterile, gauze and washed immediately with medical water. The hair is allowed to dry at room temperature.
Humidification
Keeping the recipient and donor sites moisturised promotes healing. Frequent spraying of the grafts with saline solution helps the process. Graft sites are most sensitive to trauma during the first three or four days. Keeping them moist with saline is the most important factor in soothing itching.
Scabbing
The scabs begin to fall off within 5 to 10 days after surgery.
Itching
Itching is considered a sign of healing and starts after 5 days. Using spray and aloe vera water on the transplanted area and applying aloe vera lotion on the donor area helps healing and reduces itching.
Numbness
Numbness occurs in the transplant and donor areas on the day of the procedure. In the postoperative period, numbness of the scalp in the transplant area is caused by internal swelling (oedema). Over time, the numbness decreases, and the sense of touch gradually returns.
Exercise
Avoid heavy exercise for one week. Too much activity can cause swelling, bleeding, and graft loss.
Bad hair replacement
The results of hair transplantation largely depend on the equipment and experience of the clinic and surgeon, the surgical technique applied, and postoperative care. Choosing an experienced and skilled surgeon in hair transplant surgery is very important to achieve a successful result. You can find out how important it is to work with the right physician in a good clinic in the following articles.
- A qualified surgeon can design the hairline and place the grafts to mimic natural hair growth patterns. The correct angulation and orientation of the follicular units with one or two hairs is very important for the natural appearance.
- An experienced surgeon can position the grafts appropriately and ensure that they survive the transplant, resulting in good hair growth. The surgeon must individualise and plan for each patient and perform the operation with the aim of minimising complications.
- The success of hair transplantation depends on the transplanted hair follicles receiving adequate blood supply. Poor surgical techniques can compromise blood flow, which can lead to poor hair growth or eventual loss.
- Failure to maintain good hygiene and sterile conditions can lead to infections. Infections can damage the transplanted hair follicles, which can lead to hair loss or a failed transplant.
- A qualified surgeon will ensure that the donor area from which hair follicles are taken during transplantation has a sufficient amount of healthy hair follicles. This helps prevent limited or thinning hair growth after two years.
- Hair transplant specialists can help patients set realistic expectations based on each individual's unique circumstances. The surgeon should understand the patients' goals and have the ability to meet them, providing detailed counselling to the patient in advance about the need for medical treatment and the possibility of hair transplantation in the future.
- Proper surgical techniques and postoperative care minimise the risk of complications such as infection, wound dehiscence, and effusion at the donor site.
- An experienced surgeon knows very well how to create a natural and sustainable hair transplant design.

Bad habits
Bad habits can negatively affect the results of hair transplantation by disrupting blood circulation and making the area susceptible to infection. Therefore, it is important to avoid these habits before and after hair transplantation.
Bad habits that may affect hair transplant results:
Nicotine narrows the blood vessels, making it difficult for oxygen-rich blood to reach the surgical site. This can negatively affect the survival of grafts and delay wound healing. Smoking can negatively affect hair growth and health.
Alcohol dilutes the blood, increasing the likelihood of bleeding during the surgical procedure. This can make it difficult to place the grafts and increase the risk of infection. It is important to avoid alcohol one week before and after surgery.
A diet lacking vitamins and minerals necessary for hair health can negatively affect hair growth and cause weakening of the grafts. Eating a balanced diet and drinking enough water are important for healthy hair.
Being under severe stress can lead to a temporary condition called telogen effluvium, which can cause hair loss in both transplanted and non-transplanted hair. Reducing stress levels is important to maintain hair transplant results.
If you are taking any supplements for weight training or bodybuilding, avoid taking these products one week before surgery
In addition, inadequate hygiene and failure to maintain non-sterile conditions can lead to infection. Infections can damage the transplanted hair follicles, resulting in hair loss or a failed transplant.
Infection
The risk of infection after hair transplantation is low, but it can occur. Infections can occur at both the recipient and donor sites. Infections after hair transplantation and what you need to know about them are below:
Causes of infection
Infections usually occur due to poor hygiene, excessive scabbing, or existing medical risk factors. High-tension closures can increase the risk of infection by compromising blood circulation in the donor area and causing significant scabbing. Lack of proper postoperative care can increase the risk of infection and cause damage to the hair follicles. Therefore, the care instructions recommended by the surgeon should be followed.
Signs of infection
Infections in the recipient site often present with papulopustules in the affected area. Localised areas may show redness, tenderness, and fluctuation, which may suggest abscess formation.
Infection prevention
The aseptic norms of the operation must be observed. You should make sure that your resistance is not low. You should follow the postoperative instructions for washing and wound care in detail, as failure to follow these instructions may lead to infection. Shampooing the scalp with chlorhexidine gluconate soap the night before and in the morning can reduce the risk of infection. Drugs used during hair transplant surgery may cause heartburn. If hyperacidity develops, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Treatment of infection
If infection occurs, your surgeon can administer appropriate antibiotics after sensitivity testing.
Hormonal diseases
Hormonal diseases and hormonal changes that may affect the results of hair transplantation are as follows:
- Hormonal imbalances are one of the causes of hair loss in the late period after hair transplantation. Hormonal fluctuations associated with ageing or underlying medical conditions can affect hair health. In particular, hormonal changes associated with ageing or underlying medical conditions can affect the health of the transplanted hair. It is important to eliminate hormonal imbalances.
- Androgenetic alopecia is characterised by miniaturisation of hair follicles and is associated with the action of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) on androgen receptors. It can be permanent when DHT-resistant hair follicles are transplanted.
- Primary Cicatrial Alopecia (PCA): This group includes inflammatory hair disorders characterised by loss of hair follicles and inflammation of the scalp. Frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA) is a common type of PCA and is difficult to treat.
- Finasteride reduces hair loss and increases hair growth in men. However, there are reports of potential long-term sexual side effects and depression associated with finasteride.
- Various factors such as medications, trauma, and emotional and physiological stress can lead to the development of telogen effluvium.
- Thyroid hormone levels such as TSHand free T4 can affect hair loss.
- Autoimmune disorders and hormone abnormalities can jeopardise the outcome of hair transplantation.
Loss of existing hair
The fact that the existing hair continues to fall out while the transplanted hair maintains its vitality after hair transplantation is an important issue for people who are considering or have undergone hair transplantation. The causes of this situation and the precautions that can be taken are as follows:
- Natural hair loss process,the loss of existing (non-transplanted) hair may continue independently of hair transplantation. In cases such as androgenetic alopecia (male pattern baldness), hair loss may progress due to genetic and hormonal factors.
- After the surgical procedure, both transplanted and existing hair may experience shock loss (telogen effluvium). Shock loss is usually temporary, and the hair starts to regrow within a few months.
- The use of medications such as minoxidil and finasteride after hair transplantation can help protect existing hair and promote hair growth.
- If hair loss persists, an additional hair transplant procedure may be required.
Lifestyle and nutritional
Lifestyle and nutrition are of great importance for the protection of hair after hair transplantation. Here are the things to be considered:
- It is important to follow a balanced diet that contains the vitamins, minerals, and nutrients necessary for hair health. This helps strengthen the hair follicles and promote healthy hair growth.
- Regular exercise supports hair health as well as improving overall health. Exercise increases blood circulation, helping to transport more oxygen and nutrients to the hair follicles. However, it is important to avoid excessive physical activity, especially during the recovery period.
Stress
Management of stress after hair transplantation is of great importance for the health of both transplanted and existing hair. According to sources, the effects of stress on hair and methods of coping with stress are as follows:
- Stress, anxiety, or depression can cause a temporary type of hair loss called telogen effluvium. In this condition, hair follicles enter the resting (telogen) phase faster than normal.
- This condition occurs when the hair follicles enter the resting phase (telogen) due to surgical trauma, anaesthesia, or stress, and hair loss increases. Telogen effluvium can affect both transplanted and existing hair. Shock loss can start 2-6 weeks after hair transplantation. Acute telogen effluvium usually resolves when the underlying causes are eliminated.
- A healthy person loses an average of 50-100 hairs per day. However, this number may increase under severe stress.
- In addition to causing hair loss, stress can also negatively affect overall hair health.
- Surgical procedures such as hair transplantation can cause anxiety in patients.
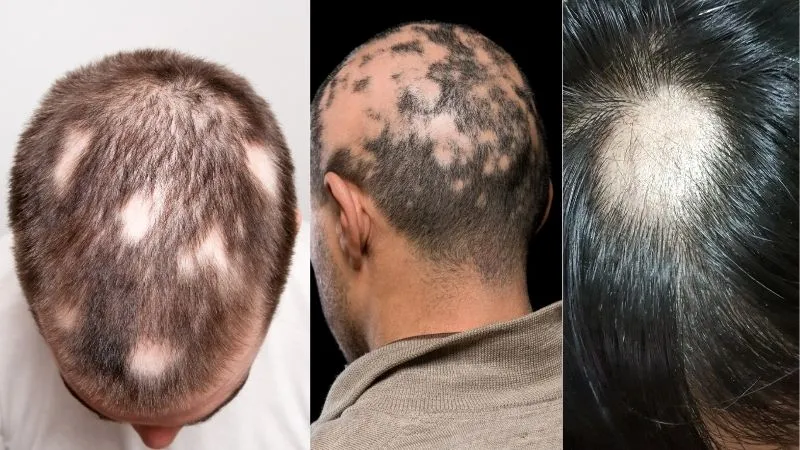
Alopecia areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that attacks the hair follicles and causes scarless hair loss and the formation of small, round bald patches. Hair transplantation is not recommended in patients diagnosed with alopecia areata.
This type of hair loss is not associated with hair transplantation. However, alopecia areata is a rare complication after hair transplantation. In case of alopecia areata after hair transplantation, both transplanted and existing hair is affected.
Medical treatments for sustaining transplanted hair
Various medical treatments are available to protect transplanted hair and promote hair growth after hair transplantation. These treatments include:

Minoxidil
- It is an FDA-approved topical medication that can be used by both men and women. It helps prevent hair loss by thickening hair follicles and accelerating hair growth. It can help the hair that falls out during shock loss after hair transplantation to grow faster.Adequate and regular sleep is essential for the body to regenerate and repair itself. Lack of sleep can increase stress levels and negatively affect hair health.
- It is important to protect the transplantation area from direct sunlight. The harmful rays of the sun can irritate the scalp and damage the hair follicles. Therefore, it is important to protect yourself by wearing a hat or sunscreen.
- Drinking enough fluids is as important for hair health as it is for the general health of the body. Adequate fluid intake regulates blood circulation and helps keep hair follicles moisturised.
Finasterid
It is an FDA-approved oral drug used only by men. It reduces hair loss and increases hair growth by blocking the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
It is an option that involves injecting platelet-rich plasma to stimulate hair follicles using the body's natural healing processes. It is used in combination with hair transplantation to stimulate hair growth and accelerate healing.
Laser treatment
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) is another method used to stimulate hair growth.
Mesotherapy
Mesotherapy is a treatment method by injecting vitamins, minerals, amino acids, enzymes, and other nutrients into the middle layer of the skin (dermis). It reduces hair loss by nourishing the hair follicles and promotes stronger and healthier hair growth. It is applied for male pattern hair loss (androgenetic alopecia) and hair weakness in women.
How to prevent hair loss after 2 years ?
The following measures can be taken to prevent hair loss 2 years after hair transplantation:
- Regular use of medications such as minoxidil and finasteride after hair transplantation can help protect existing hair and promote hair growth.
- Elimination of hormonal changes can positively affect hair health. If necessary, consult a doctor and have your hormonal levels checked.
- Being under severe stress can lead to telogen effluvium, which can cause hair loss in both transplanted and non-transplanted hair. It is important to use stress management techniques to reduce stress levels.
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively affect hair health by disrupting blood circulation. Therefore, it may be beneficial to avoid or reduce these habits.
- Using gentle shampoos and conditioners suitable for your hair type protects the scalp and hair fibres.
- It is important to avoid excessive heat applications (hair dryer, straightener, etc.) and chemical treatments (dye, perm, etc.) that can damage the hair.
- Carefully following the postoperative care instructions given by the surgeon reduces the risk of infection and ensures healthy growth of hair follicles.
- It is important to remember that hair transplant results may vary from person to person, and it may take time to achieve full results.
- The combination of these precautions can help ensure the longevity of the results obtained after hair transplantation and prevent hair loss.
